(Figure adapted from Duffy et al. (2018) Wiley Interdiscip Rev)
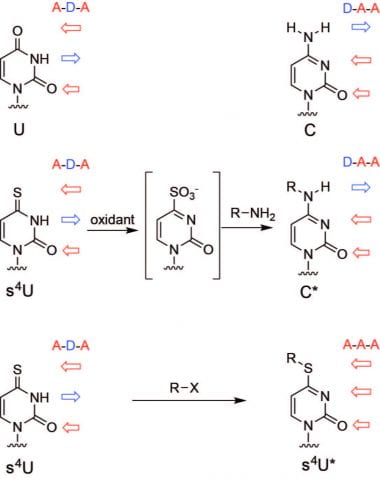
TimeLapse-seq. We have developed chemical methodologies to track RNA population dynamics from transcription to degradation using metabolic labeling with thiolated nucleotides (s4U and s6G). Traditionally, thiolated RNAs are identified using biochemical enrichment with the assistance of activated disulfides (reviewed in 1). To improve enrichment, we developed efficient methane thiosulfonate (MTS) chemistry to biotinylate thiolated RNA (2), and solid phase MTS chemistry to directly and covalently capture thiolated RNA on beads (3). Alternatively, to avoid the need for biochemical enrichment, we developed a nucleotide recoding approach to identify new transcripts directly in a sequencing experiment (TimeLapse-seq, ref 4). In TimeLapse-seq, the Watson-Crick hydrogen bonding patterns of thiolated bases are recoded using oxidative nucleophilic aromatic substitution chemistry. This leads s4U to be recoded into a C analogue (4), and s6G can be recoded into an A analogue (5), allowing identification of metabolically labeled transcripts directly in a sequencer. Ongoing work includes the development of additional nucleotide recoding chemistries and the application of these approaches to a wide range of biological systems.
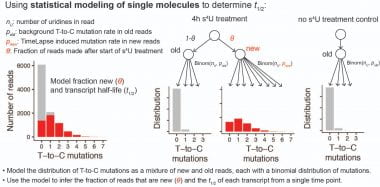
We use Bayesian statistical modeling to quantify degradation rates from TimeLapse-seq data (figure below). Want to simulate TimeLapse data? Play with our shiny app to better understand sequencing depth/format requirements to get good degradation rate estimates and to plan your experiment.
 (Figure adapted from Duffy et al. (2018) Wiley Interdiscip Rev)
(Figure adapted from Duffy et al. (2018) Wiley Interdiscip Rev)
- Duffy, E. E., Schofield, J. A., & Simon, M. D. (2018). Gaining insight into transcriptome-wide RNA population dynamics through the chemistry of 4-thiouridine. Wiley RNA, e1513.
- Duffy, E. E., Rutenberg-Schoenberg, M., Stark, C. D., Kitchen, R. R., Gerstein, M. B., and Simon, M.D., (2015) Tracking distinct RNA populations using efficient and reversible covalent chemistry. Mol Cell, 59(5), 858-66. PMID: 26340425.
- Duffy, E. E., Canzio, D., Maniatis, T., & Simon, M. D. (2018). Solid phase chemistry to covalently and reversibly capture thiolated RNA. NAR, 46(14), 6996–7005.
- Schofield, J. A., Duffy, E. E., Kiefer, L., Sullivan, M. C., & Simon, M. D. (2018). TimeLapse-seq: adding a temporal dimension to RNA sequencing through nucleoside recoding. Nature Methods, 150, 279.
- Kiefer, L., Schofield, J. A., & Simon, M. D. (2018). Expanding the Nucleoside Recoding Toolkit: Revealing RNA Population Dynamics with 6-Thioguanosine. JACS, 140(44), 14567–14570.